What is the Endocannabinoid System?
The Endocannabinoid System : Revolutionary Medical Discovery
Many doctors and researchers believe the discovery of the endocannabinoid system could be one of the most exciting scientific discoveries of our time. To understand how and why cannabis seems so helpful to mammals (like humans and dogs), knowing about the this system is key.
There is still much more to discover regarding how this complex system functions, but so far researchers have determined that endocannabinoid receptors are found embedded in cell membranes throughout the body. There are two distinct cannabinoid receptors:
- CB1, located throughout the nervous system, connective tissues, gonads, glands, and organs
- CB2, predominantly found in the immune system and its associated structures.
Many tissues contain both CB1 and CB2 receptors, and there is speculation that there may even be a third receptor, as of yet undiscovered.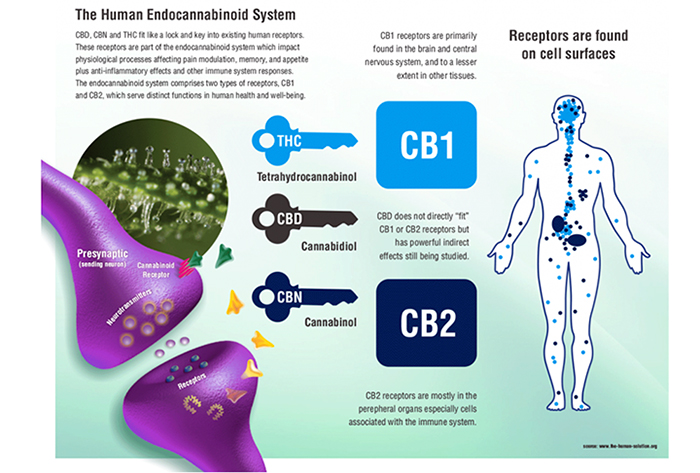
Noteworthy Facts About the Endocannabinoid System
- All mammals have an endocannabinoid system.
- Regulates immune and nervous system.
- Promotes general homeostasis in the body.
- Is comprised of cannabinoid receptors, which are located throughout the body – the brain, organs, connective tissues, glands, and immune cells.
- Cannabinoids promote homeostasis in a number of ways. One way is through autophagy, the process that regulates “cell death”. This has a powerful impact on the cell’s ability to recognize healthy cells and keep them alive, or to recognize “bad” ones like cancer, and self-destruct.
- The endocannabinoid system is a master communicator between different types of cells in the body.
- For example, if you are injured, the cannabinoids in your body can rally to act on the nerve cells, preventing over-firing of an inflammatory response.
- Cannabinoids have a calming influence on immune cells. The result of this communication among the three various types of cells is a reduction in pain and inflammation.
How Your Internal (Endo) Cannabanoid System Works
When in an optimal state, the human body is balanced, and produces both the lock and the key, so to speak, for many systems within the body.
This system of receptors is one such example, having its counterpart in what are called endo-cannabinoids. These tiny molecular structures fit into the receptors of the endocannabinoid system like keys fitting into a lock. The root word “endo” means “within”.
The two most well-known of the endocannabinoids are anandamide (a.k.a. “the bliss molecule”) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG).
The first endocannabanoid, anandamide, is named after the Sanskrit word for “bliss”, so named because it is the molecule believed to produce a heightened sense of happiness. Other functions regulated by anandamide include memory, appetite regulation, higher thought processes, movement control, fertility, pain, and cancer cell destruction. It is for this reason that some practitioners refer to anandamide as our body’s innate resilience against depression and anxiety.
Like all neruotransmitters, anadamide is fragile and breaks down quickly. CBD binds to CB1 receptors and this produces the enzymes responsible for the break-down of anandamide. This is only a simplistic explanation of how CBD mediates the THC compound in cannabis. Again, THC is the compound responsible for the psychoactive effects, a.k.a. the “high”, of cannabis. So in other words, CBD, including the CBD found in dietary supplements, neutralizes the psychoactive effects of THC.
The second molecule, arachidonoylglycerol or 2-AG, is a member of a group of molecules derived from arachidonic acid and molecule groups EPA and DGLA. These molecules, known as eicosanoids, are all oxidized versions of 20-carbon (containing 20 carbon atoms per molecule) EFAs. These molecular groups play a complex and important role in immunity and inflammation.
External Cannabanoids Also Play An Important Role in Supporting Your Health
Then there are both natural and synthetic cannabinoids found outside of the body. Phyto-cannabinoids (like CBD) are derived from plants, and can also influence and stimulate the cannabinoid receptors. The root word “phyto” means “of a plant or relating to plants”. Pharmaceutical companies have also been able to isolate and synthesize cannabinoids.
What About the Cannabis Sativa Plant?
Of ALL the plants on God’s green earth, cannabis sativa is the plant with the most phytocannabinoids. Other plants that produce them include black pepper, echinacea, truffle mushroom, clove, and many herbs and spices. The antioxidant properties protecting leaves and flowers from ultraviolet radiation are… you guessed it, cannabanoids. In no uncertain terms cannabanoids neutralize harmful free radicals generated by the sun’s UV rays, thus protecting the plant’s cells. Antioxidants found in plants have long been used in supplements to combat the damage of free radicals.
CBD, a.k.a. cannabidiol, is just one of the major cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant. Recently CBD is getting a lot of press due to its anti-inflammatory, anti-spazmotic, anti-tumor, anti-depressant, anti-oxidant, and probably a number of similar “anti” properties.
Opinion on Pharmaceutical Derived Cannabanoids
It is our belief that a full-spectrum cannabinoid profile is more beneficial than isolated synthetic compounds. We adhere to the wisdom that ultimately nature is more intelligent than humans. The array of phytocannabinoids found in the cannabis plant is unparalleled and works synergisticly way with the body. More and more scientific and medical research is added each day to support this notion.
These are exciting times as we discover new systems in our bodies and ways to support our personal balance and health.
The Truth Will Set You Free
If you are anything like me, you might start to wonder how this plant is capable of performing so powerfully in the body? Is it true? Because from the outside, it kind of sounds far fetched. Don’t take our word for it then! Did you know you can use the PubMed.gov website to search scientific journal articles by keyword topic? The United States government has made the content from thousands of scientific journals published in the last 20 years available for the public to peruse online.
If you go to PubMed.gov site and search for the word “cannabis” you would get approximately 8,637 results. Add the word “cannabinoid,” and the results increase to approximately 20,991 articles. Clearly there is no shortage of scientific research pertaining to cannabis and it’s medicinal benefits. The list of different medical conditions’ response to cannabis is staggering. Just a few include inflammation, cancer, arthritis, epilepsy, anxiety / depression, and skin conditions.
Depending on your incentive to dig deeper, your first step in understanding the miracle of medical cannabis is to discover the Endocannabinoid System.
Even with over 20,000 PubMed articles related to cannabis, we have still only begun to scratch the surface of learning how cannabis works in our bodies.
While we encourage you to empower yourself with knowledge, the fact is that you could research until the cows come home. In the meantime, your health is declining and you or someone you know is suffering needlessly. So we also want to encourage you to listen to your intuition / guy and once you’ve reached a reasonable threshold, be the change and TAKE ACTION.
Learn how you can:
a.) Start feeding yourself world-class doses of nano-enhanced CBD oil (ASAP) and/or
b.) Be a smart person ahead of the trend and get involved in the exploding cannabis industry now.
Thanks for reading and if you liked this post, please like and share!

Leave a Reply